Contents
- 1. The Influence of Psychology in Cannabis Consumption
- 2. Historical Psychology and Cannabis Usage
- 3. Philosophical Psychology: How Cannabis Reflects Society’s Morality
- 4. Strategies Employed by Brands, Dispensaries, and Legislators
- 5. Customer Purchase Behaviors and Psychological Influence
- 6. Future Trends: Psychological and Compliance-Based Labeling
- 7. Glossary
- 8. Quiz
The Influence of Psychology in Cannabis Consumption
Psychological principles such as reinforcement, cognitive dissonance, and reward-seeking behavior are at the heart of consumer interaction with cannabis products. The decision to purchase, consume, or continue using cannabis is often driven by a desire to relieve stress, anxiety, or pain, aligning with operant conditioning principles where relief becomes the reward.
Did You Know?
The human brain has cannabinoid receptors in areas associated with pleasure, memory, and time perception, making cannabis a unique psychoactive substance in how it impacts mental states.
Historical Psychology and Cannabis Usage
The use of cannabis has evolved with societal changes, particularly influenced by historical and cultural shifts. Historically, the stigma of cannabis was based on racial and political manipulation, but as perceptions changed, so did its use and legal status. Historical psychology examines how previous generations used cannabis both for medicinal and recreational purposes.
Philosophical Psychology: How Cannabis Reflects Society’s Morality
Philosophical psychology addresses the moral and ethical aspects of cannabis. Many advocates argue that cannabis promotes well-being and should be part of holistic healthcare, while opponents raise concerns over its addictive qualities. The debate ties back to broader societal discussions on freedom, personal responsibility, and morality.

Did You Know?
Cannabis was widely used in the 19th century in Western medicine until its prohibition in the early 20th century, largely as a result of perceptions of drug use. In other words, policymaking involves deliberate psychological tactics, so cannabis is only criminalized or embraced as a result of psychology.
Strategies Employed by Brands, Dispensaries, and Legislators
Cannabis companies and legislators apply a range of psychological tactics to influence behavior. Brands use packaging, pricing, and promotions to create an emotional connection with consumers, while dispensaries focus on customer experience and education. Legislators leverage compliance and labeling to ensure consumer safety and to align with broader societal values regarding responsible cannabis consumption.
Customer Purchase Behaviors and Psychological Influence
Brands often employ scarcity marketing or highlight specific effects like “relaxation” or “focus” on packaging to appeal to psychological drivers like FOMO (fear of missing out) or specific needs. Dispensaries might train budtenders to suggest certain products that cater to customers’ psychological desires for pain relief or relaxation.
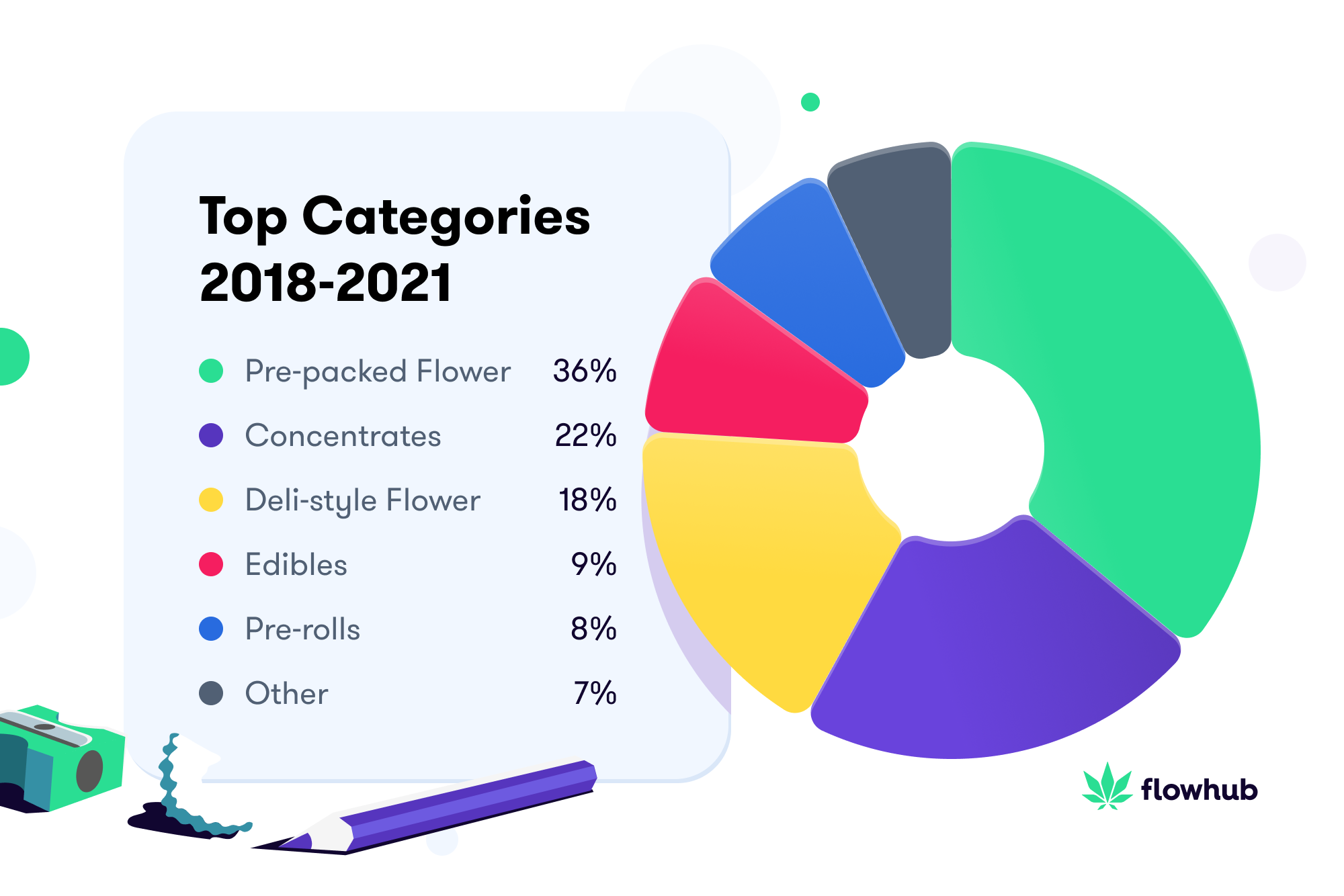
Another way to look at the psychology of purchasing behaviors is to look at why people are buying what it is they’re buying. Example: in mid-2022, the number one category across the industry was “pre-packed flower” (Pre-Rolls). Why? Psychology. See, prior to COVID consumers had no problem going to the local dispensary. Because COVID instilled a new mindset in the people–one that emphasized social distancing, masks, and self-quarantine, consumers had to engage in alternative methods of logistics and distribution 😉. Namely, having access to marketplaces via delivery.
Did You Know?
The idea for The Budtenders Ethos is, in part, inspired by the creation of cannabis delivery services in northern California, where we partnered with a local company called CaliKosher, a fully-integrated, full-service cannabis company, to bring cannabis delivery to rural patients.
6. Future Trends: Psychological and Compliance-Based Labeling
In the next decade, the cannabis industry is expected to see a stronger alignment with psychological and compliance-based labeling, where packaging will emphasize transparency and the benefits of products in alignment with health and wellness trends. The introduction of blockchain for compliance, tracking products from seed to sale, could also reshape consumer confidence and purchasing behaviors.
7. Glossary
- Operant Conditioning
- A learning process where behavior is controlled by consequences like rewards or punishments.
- Cognitive Dissonance
- A psychological state where an individual experiences conflict between their beliefs and actions, often leading to attitude changes.
- FOMO (Fear of Missing Out)
- A psychological trigger where individuals feel anxiety over missing out on rewarding experiences or opportunities.
- Reinforcement
- The process of encouraging or establishing a pattern of behavior, typically through reward.
- Compliance
- Adherence to laws, regulations, or guidelines, particularly important in the cannabis industry due to strict legal frameworks.
- Holistic Healthcare
- A wellness approach that considers the whole person—mind, body, spirit—rather than just symptoms of disease.

Quiz
Test your knowledge on the psychological aspects of cannabis. Select the best answers:
- Which psychological principle is most associated with the consumer habit of seeking cannabis to relieve stress?
- Cognitive Dissonance
- Operant Conditioning
- Reinforcement
- How do brands typically appeal to consumers’ FOMO?
- By highlighting scarce or limited-time offers
- By emphasizing long-term benefits of the product.
Members Lounge
Want to Know More? Subscribe for Free!
For access to exclusive information found only here at BTE, sign up for our free membership!


Leave a comment